Rocks are split into one of two categories based upon various factors. These two types of rock, which include felsic and mafic rocks, are important for distinguishing between volcano types and depositional environments.
A few Helpful Terms:
Viscosity: Viscosity is a measurement of how resistant a liquid is to flowing. For instance, water has a very low viscosity, meaning it flows very easily while honey has a high viscosity, meaning it flows very slowly.
Explosivity: A measurement of how explosive a volcanoes eruption is, with high explosivity being very explosive while flowing like honey and low explosivity meaning the lava flows like cement and is not very dangerous.
Magma vs lava: both are forms of liquid rock; that is rock before it is solidified, with lava being liquid rock on the surface of the earth and magma being liquid rock underground.
Volcano: A volcano is a break in earths crust that allows gasses and hot magma to escape from below to the surface. Below is a diagram of the anatomy of a volcano.
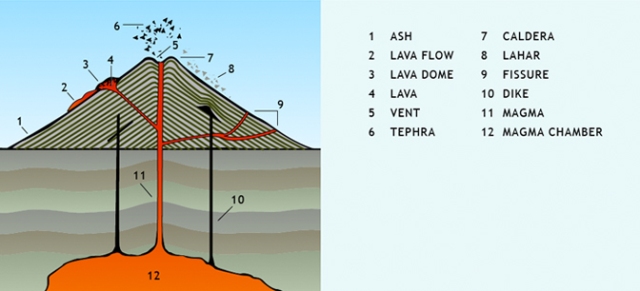
Types of Rock:
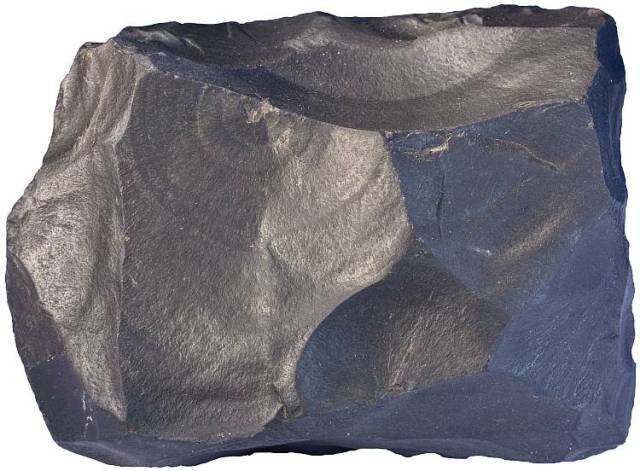
Mafic Magmas: The rocks that form from this type of magma are representative of the ocean sea floor. They tend to have high iron content or are composed of other heavy metals and elements. As a result these magmas are quite dense in comparison with felsic magmas. Mafic rocks are also often distinguished by their dark color. Before cooling, mafic lava has a very low viscosity. The below picture is of the mafic rock basalt.

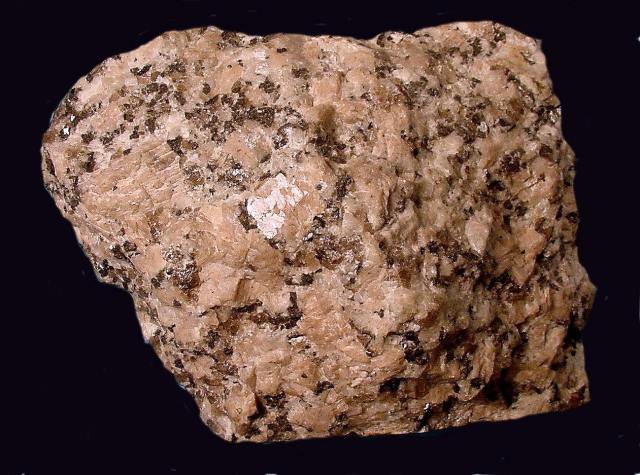
Felsic Magmas: The rocks that form from this type of magma are representative of continental rocks. They tend to have high Silicon content, also known as Silica content. In addition to silicon, felsic lavas also contain other light elements, such as oxygen, sodium, potassium and aluminum. Before cooling, felsic magmas have a very high viscosity. These types of rocks are generally light colors as well. In comparison with mafic rocks, felsic rocks are much lighter and as a result “float” higher in the lithosphere then mafic rocks. This is why continental rocks are felsic and oceanic rocks are mafic. The below picture is of the felsic rock granite.

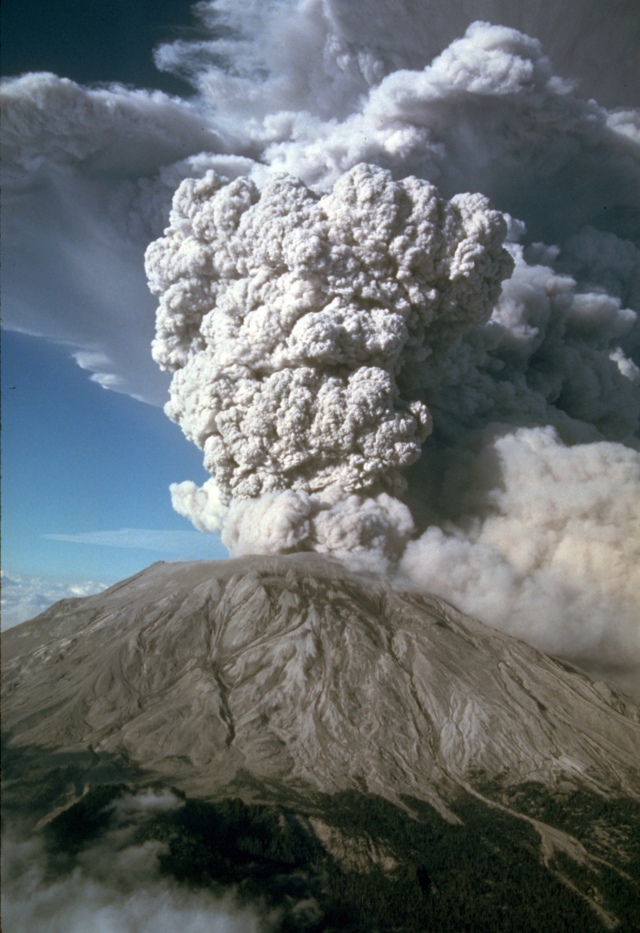
Types of Volcanoes:
Mafic Volcanoes: volcanoes that produce mafic lava have a very low explosivity due to the how easily the lava flows and how few volatiles (such as oxygen and silicon) are present within the lava. This forms shield volcanoes, which are gently sloping large volcanoes like those in Hawaii. These tend to be one of the least dangerous forms of volcanoes. The picture below shows a volcano in Hawaii, people are in the back ground showing just how safe these types of volcanoes are in comparison to felsic volcanoes.

Felsic Volcanoes: Volcanoes that produce felsic lavas have very high explosivity due to their high concentrations of volatiles such as silicon and oxygen. The high viscosity of the lava also makes felsic volcanoes highly explosive, causing the lava to “clot” the mouth of the volcano. This builds up pressure until the volcanoes explodes. Felsic lava forms Stratovolcanoes which are tall, steep volcanoes. This is one of the deadliest types of volcanoes for humans. Examples of this type of felsic volcano are Mount Vesuvius and Mount Saint Helens. Both these volcanos are notorious for how explosive and deadly their eruptions where. The below picture is of Mount Saint Hellens, the ash billowing from the mount of the volcano shows just how deadly these volcanoes are.

